Speaking Clearly using the Awareness Wheel
Psychologists have studied what effective communication looks like for married couples for decades. After uncovering what factors contribute to effective communication, some clever people have combined these ideas into a simple model that we share here. This model is known as the Awareness Wheel and Listening Cycle. Communication skills can improve all kinds of relationships. We hope you find this short tutorial useful and even purchase the book if you would like to learn more.
Before we explain Awareness Wheel and Listening Cycle communication, here are some simple ground rules for communication in general:
Rules for the both of you:
- The speaker has the floor. Don’t cut off the speaker or finish his or her sentences.
- Share the floor (take turns)
- No problem solving
Speaker:
- Say “I” statement, Speak for self
- Share your feelings without putting down your friend
- Be specific and brief about your perceptions and feelings (2 - 3 sentences)
- Stop and allow your listener to paraphrase (if the paraphrase is not accurate, politely restate what was not heard the way you intended it.)
Listener:
- Choose a “Caring Connection” emotional brain state. You won’t be able to listen effectively if you are in a protective emotional state like “Anger”, “Fear” or “Panic”. See the Feeling Words List
- Say “You” statements providing a summary of what you heard the speaker say. (The speaker gets the focus)
- Don’t rebut (refute by evidence or argument) but instead paraphrase what the speaker said. Focus on the speaker’s message (Don’t offer your thoughts yet. Wait until you have the floor.)
- Invite the speaker to correct saying “Is that right?” or add more saying “Tell me more.”
Below is the Awareness Wheel Diagram as presented by:
Miller, Sherod, Phyllis Miller, Elam W. Nunnally, and Daniel B. Wackman. Talking and Listening Together: Couple Communication I. Littleton, Colo.: Interpersonal Communication Programs, 1991. Print.
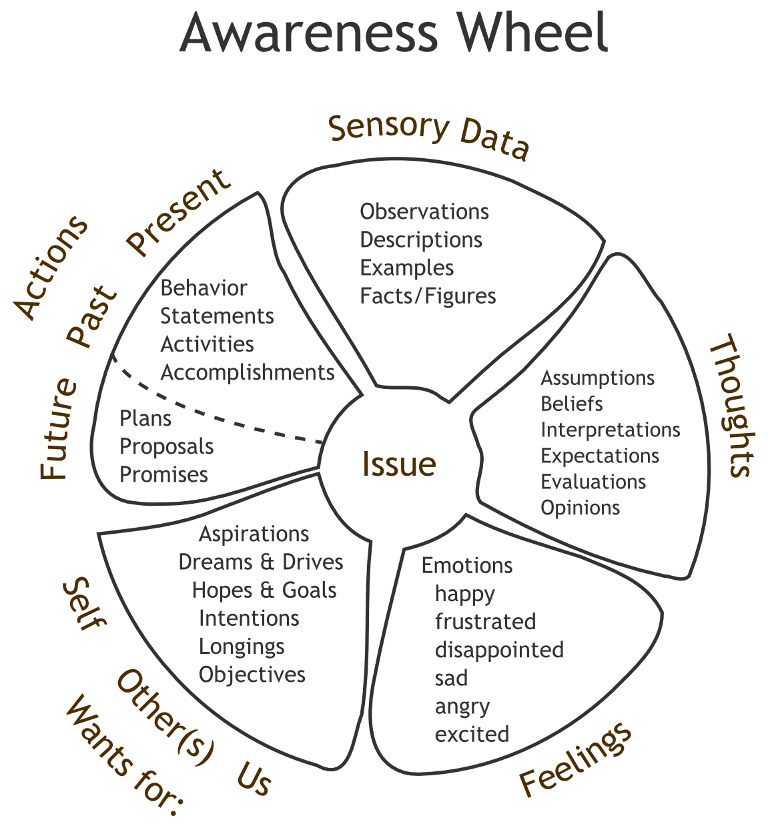
Awareness Wheel:
The Speaker (from above) will be most complete in his description of an issue if he explains his full awareness. Starting from Sensory Data, the speaker can move clockwise around the circle to avoid confusion about how he stands on any issue.
When speaking, talk through your Awareness wheel using the first person, “I” statements.
Sensory data
Information gathered using your senses: sight, sound, smell, taste, touch
External data: The data you gather from other people. Verbal, but mostly nonverbal, behaviors: facial expressions, gestures, movement, posture, scent, tones, words
Intuitive sensations: memories, associations, insights, hunches, dreams, intuitions Bodily sensations: goose bumps, a chill, fatigue, stomach tightness, headache
Thoughts
The meanings you make out of the sensory data you receive - eg. beliefs, interpretations, expectations
Words that signal thinking processes: assumptions, benefits, conclusions, evaluations, guesses, reasons, ideas, impressions, judgments, metaphors, needs, objections, opinions, predictions, principles, values. NB: Influence of Family of Origin, cultural, societal & gender ’norms'
Feelings
Your responses to your interpretation of thoughts, sensory data & wants in a situation. You can use the brain state feeling word list to describe what you’re feeling
Wants
Your desires for yourself and for others, short or long term, general or specific Includes: aspirations, dreams, drives, goals, hopes, intentions, longings, objectives
Actions
What you say and do in response to sensory data, thoughts, feelings and wants - relates to past, present, and future.
Actions result from how you process sensory data, thoughts, feelings, and wants Activities, agreements, commands, commitments, contracts, promises, words
